Sports Gesture Classification1: Set up Docker Container
- Introduction to Docker
- Install Docker Server & Client
- Write Dockerfile
- Create a Docker Container
- Training on docker
- Downloading the Model from Docker to Local
- Saving the Docker Image
- Refer
From Kaggle: Sports Gesture Classification Competition, I would use SwinTransformer from Timm to build an inference API and set it on a container
- Github: Sports Gesture Classification on Docker
- Demo for training and api prediction on Docker
Introduction to Docker
Docker is a software platform that allows you to create and manage containers. A Docker image contains all the necessary files and dependencies to run an application, while a container is a running instance of that image. Containers provide an isolated and reproducible environment for running applications. 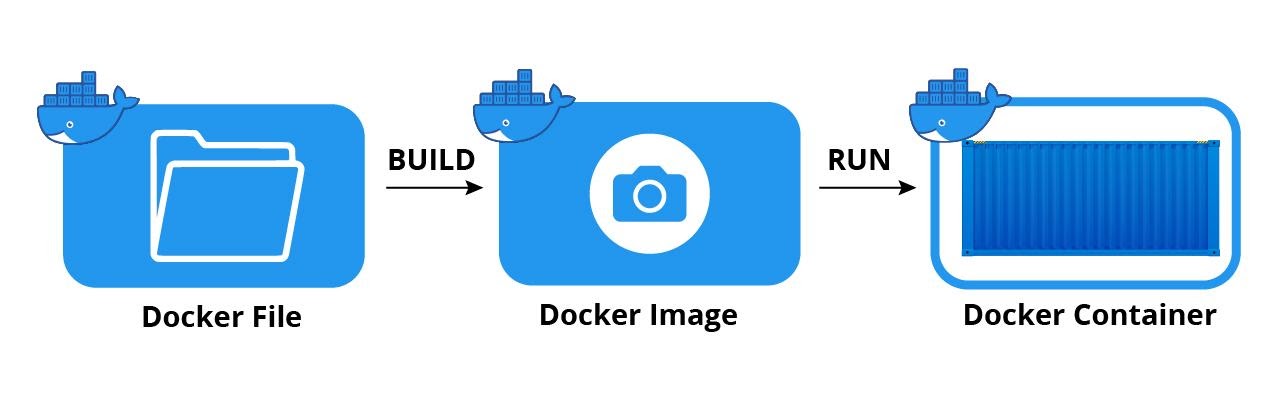
For docker container, it is similar to the virtual machine platform, except Docker is an operating system for containers. And the hardware source (ex. RAM, GPU) is used from the local. 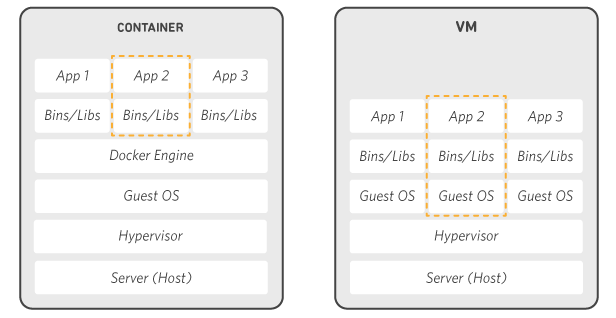
Install Docker Server & Client
First, you need to install Docker Server & Client on your system. Follow these steps:
Remove any previously installed Docker components:
sudo apt-get purge docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-buildx-plugin docker-compose-plugin docker-ce-rootless-extras sudo rm -rf /var/lib/docker sudo rm -rf /var/lib/containerdInstall Docker
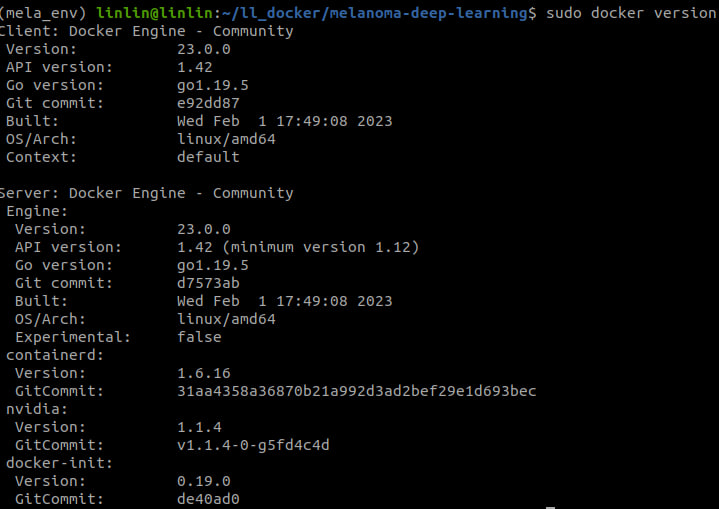
sudo apt-get install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io docker-compose-pluginVerify the Docker installation by checking the version by checking
docker versionin terminal
Make sure the version information is displayed correctly as following.
Write Dockerfile
A Dockerfile defines the steps and packages required to build the platform for your sports classification project. Here’s an example Dockerfile.
FROM ubuntu:latest
RUN apt-get update && apt-get install -y git && \
apt-get install -y python3-pip sudo vim wget && \
rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
# The -m option of useradd command allows to copy all files from your system skeleton directory (/etc/skel) to the newly created home directory.
RUN useradd -m linlin
# chown: add another layer on image
# chown -R <past_owner>:<current_owner> the target directory
RUN chown -R linlin:linlin /home/linlin/
# COPY --chown=<user>:<group> <hostPath> <containerPath>
# do not copy environment into docker file, add environment path into `.dockerignore`
COPY --chown=linlin . /home/linlin/sport_gesture_classification_on_docker/
USER linlin
RUN cd /home/linlin/sport_gesture_classification_on_docker/ && pip3 install -r requirements.txt
WORKDIR /home/linlin/sport_gesture_classification_on_docker/
Let’s break down this Dockerfile:
- It starts with the base image
ubuntu:latest, which provides an Ubuntu-based environment and related packages. - Necessary packages such as
git,python3-pip,sudo,vim, andwgetare installed. - A system user named
linlinis created with a home directory. - The local project files are copied to the Docker image, specifically to
/home/linlin/sport_gesture_classification_on_docker/. Make sure to add any necessary files or directories to.dockerignoreto exclude them from the copy process, ex, virtual environment path. - The user permissions are switched to linlin.
- The project’s dependencies are installed using
pip3within the project directory. - The working directory is set to
/home/linlin/sport_gesture_classification_on_docker/, which will be the default directory when the container starts.
For more details, you can go to check: Dockerfile in Sports Gesture Classification on Docker
Create a Docker Container
Build the Docker image by executing the following command in the same directory as the
Dockerfile# build image docker build -t sports_api:v1 .Here
sports_api:v1is the name and tag you assign to the image. The.indicates that theDockerfileis present in the current directory.Building the image may take some time, and the resulting image size will be around 8.7 GB. You can use
docker imageto check the available images.
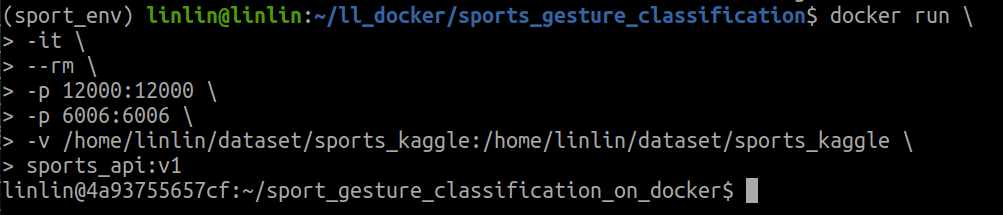
Generate a container based on the built image
docker run \ -it \ --rm \ -p 12000:12000 \ -p 6006:6006 \ -v /home/linlin/dataset/sports_kaggle:/home/linlin/dataset/sports_kaggle \ sports_api:v1Here’s an explanation of the command:
-tenables the pseudo-terminal (TTY) for the container.-iallows an interactive connection with the container.-p host_port:container_portmaps port 12000 for the Flask API and port 6006 for checking events in TensorBoard.-v $host_path:$container_pathmounts the local dataset directory/home/linlin/dataset/sports_kaggleinto the container at the same path, allowing access to the dataset from within the container.sports_api:v1refers to the image name and tag.
After executing this command, you will enter an interactive terminal located inside the Docker container.
 You can use
You can use docker psin the local terminal to check the available Docker containers.
Training on docker
On the Docker terminal, the required packages and applications have already been installed according to the Dockerfile. To train your model, run the following command:
python3 train.py
This command is the same as what you would run locally.
Checking the Training Process using TensorBoard
To monitor the training process using TensorBoard:
- Run the following command on the container to start TensorBoard:
python3 -m tensorboard.main --logdir=. --bind_all - On your local machine, access TensorBoard by visiting
localhost:6006in your web browser. This is possible because you mapped port 6006 of the container to port 6006 on your local machine during the docker run command.
Set up the API
To set up the API on the container:
- Run the following command on the container:
python3 api.py- From my view, we should not use config file to set up variables (e.g, what is the inference model?) when runing an api script, because those changable variables should be from the front end choice
- On your local machine, access the API by visiting
localhost:12000in your web browser.
Downloading the Model from Docker to Local
To download the model from the Docker container to your local machine, use the following command:
sudo docker cp <container_id>:<mnodel_path_on_docker> <local_path>
Replace <container_id> with the ID of the Docker container, <model_path_on_docker> with the path to the model file within the container, and <local_path> with the desired destination on your local machine.
Saving the Docker Image
To save the Docker image for future use on any platform, follow these steps:
- Run the following command:
docker save myimage:<tag> | gzip > docker_image_sports_api.tar.gz - The Docker image will be saved as docker_image_sports_api.tar.gz. You can now transfer and use this image on other platforms.
Refer
- This project is inspired by How to train a deep learning model using docker?
- Fask API Setting refers to https://github.com/abhishekkrthakur/sportsnoma-deep-learning
- Kaggle: Sports Gesture Classification
- Kaggle Sports Gesture Competition: SwinTransformer from Timm
- Official Docker Introduction
